In the realm of modern lighting, LED technology has revolutionized the way we illuminate our spaces, offering unparalleled energy efficiency, long-lasting performance, and versatility. One of the key advantages of LED lighting is the ability to precisely control and adjust the brightness levels, a process known as dimming. This article delves into the illuminating world of LED dimming methodologies, shedding light on the various techniques, their advantages, applications, and considerations for choosing the right approach.
Dimming LEDs is a crucial aspect of creating dynamic and energy-efficient lighting solutions. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that rely on voltage to control brightness, LEDs operate on a different principle. As semiconductor devices, LEDs emit light when an electrical current passes through them, and to dim an LED, the amount of current flowing through it must be regulated. This is achieved through specialized dimming methods and compatible LED drivers.
Understanding LED Dimming Methodologies
There are two primary methodologies for dimming LEDs: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and Constant Current Reduction (CCR), also known as analog dimming. Each method has its unique advantages and applications, catering to different lighting requirements and scenarios.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Dimming
PWM dimming is one of the most widely used and effective techniques for dimming LEDs. In this method, the LED is rapidly turned on and off at a high frequency, creating the illusion of dimming. The ratio of the on-time to the off-time determines the perceived brightness. For example, if the LED is on for 50% of the time and off for the remaining 50%, it will appear to be dimmed to 50% of its maximum brightness.
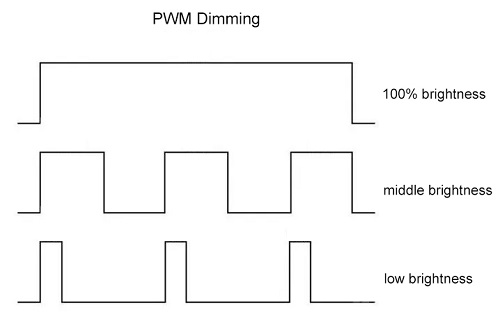
PWM dimming offers several advantages:
- Consistent Color Temperature: Since the LED is either fully on or fully off, the color temperature remains consistent throughout the dimming range, ensuring accurate color rendering. This is particularly important in applications where color accuracy is critical, such as theaters, museums, and architectural lighting.
- Smooth Dimming: PWM dimming provides a smooth and flicker-free dimming experience, making it suitable for applications where precise light control is required.
- Energy Efficiency: By reducing the on-time of the LED, PWM dimming can significantly reduce energy consumption, contributing to overall energy savings.
PWM dimming is widely used in various applications, including residential lighting, commercial spaces, and entertainment venues, where color accuracy and smooth dimming are essential.
Constant Current Reduction (CCR) or Analog Dimming
In the CCR or analog dimming method, the current flowing through the LED is gradually reduced, resulting in a corresponding decrease in brightness. Unlike PWM dimming, where the LED is rapidly switched on and off, analog dimming provides a continuous and steady light output.
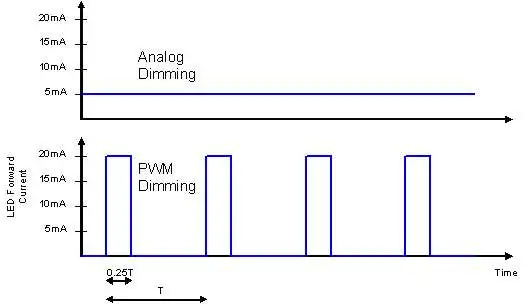
Analog dimming offers the following advantages:
- Flicker-Free Operation: Since the LED remains continuously on, analog dimming eliminates the potential for visible flicker, making it suitable for applications where flicker can be problematic, such as video recording or environments with sensitive equipment.
- Simple Implementation: Analog dimming can be implemented using relatively simple circuitry, making it a cost-effective solution for basic dimming applications.
However, analog dimming also has some limitations:
- Potential Color Shift: As the current decreases, the color temperature of the LED may shift slightly, affecting the color rendering accuracy at lower dimming levels.
- Limited Dimming Range: Analog dimming typically has a more limited dimming range compared to PWM dimming, as the LED’s brightness cannot be reduced below a certain threshold.
Analog dimming is commonly used in residential and commercial lighting applications where color accuracy is less critical, and a simple, flicker-free dimming solution is desired.
Advanced Dimming Protocols and Techniques
In addition to PWM and analog dimming, there are advanced digital dimming methods and protocols that offer more sophisticated control and integration capabilities. These include:
- DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface): DALI is a digital protocol that allows individual control and monitoring of each LED fixture in a lighting system. It enables advanced features such as scene setting, scheduling, and energy monitoring.
- DMX (Digital Multiplex): DMX is a widely used digital protocol in the entertainment and architectural lighting industries, allowing precise control over individual LED fixtures or groups of fixtures.
- 0-10V Dimming: This analog dimming method uses a low-voltage control signal (0-10V) to adjust the brightness of LED drivers, providing a simple and cost-effective dimming solution for basic applications.
These advanced protocols and digital dimming methods are often employed in large-scale lighting installations, such as commercial buildings, theaters, and architectural projects, where precise control, integration, and advanced features are required.
Choosing the Right LED Dimming Method
When selecting an LED dimming method, several factors should be considered, including the application, desired dimming performance, energy efficiency requirements, and compatibility with existing lighting control systems. It is essential to choose LED fixtures and drivers that are specifically designed for the chosen dimming method to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
Additionally, it is crucial to follow manufacturer recommendations and guidelines for proper installation and configuration of LED dimming systems to avoid potential issues such as flickering, color shifts, or premature failure of the LED components.
Applications and Considerations
LED dimming methodologies find applications across a wide range of sectors, each with its unique requirements and considerations:
- Residential Lighting: In residential settings, simplicity and cost-effectiveness are often prioritized, making analog dimming or basic PWM dimming suitable choices. However, for high-end residential projects or smart home integrations, advanced protocols like DALI or wireless dimming solutions may be preferred.
- Commercial and Office Spaces: Commercial and office environments often require energy-efficient and flexible lighting solutions. PWM dimming or advanced protocols like DALI or 0-10V dimming can provide precise control and integration with building automation systems.
- Hospitality and Retail: In hospitality and retail settings, creating the right ambiance and mood is crucial. PWM dimming or advanced protocols that allow for scene setting and color control may be preferred to enhance the customer experience.
- Entertainment and Architectural Lighting: In theaters, concert venues, and architectural lighting projects, color accuracy, smooth dimming, and precise control are paramount. PWM dimming or digital protocols like DMX are often the preferred choices in these applications.
- Industrial and Outdoor Lighting: In industrial and outdoor settings, factors such as durability, reliability, and compatibility with existing infrastructure play a significant role. Analog dimming or robust PWM dimming solutions may be more suitable in these environments.
Conclusion
The world of LED dimming methodologies offers a wide range of options to meet the diverse needs of various lighting applications. From the smooth and color-accurate PWM dimming to the flicker-free analog dimming, and the advanced digital protocols, each method has its unique advantages and applications. By understanding the principles behind these dimming techniques, lighting designers, architects, and homeowners can make informed decisions to create the perfect ambiance and achieve energy efficiency while enjoying the benefits of LED technology.
As LED technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative and sophisticated dimming methodologies to emerge, further enhancing our ability to control and shape the illumination of our environments. Staying informed about the latest advancements and industry best practices will be crucial in harnessing the full potential of LED dimming for creating dynamic, energy-efficient, and visually stunning lighting solutions.
